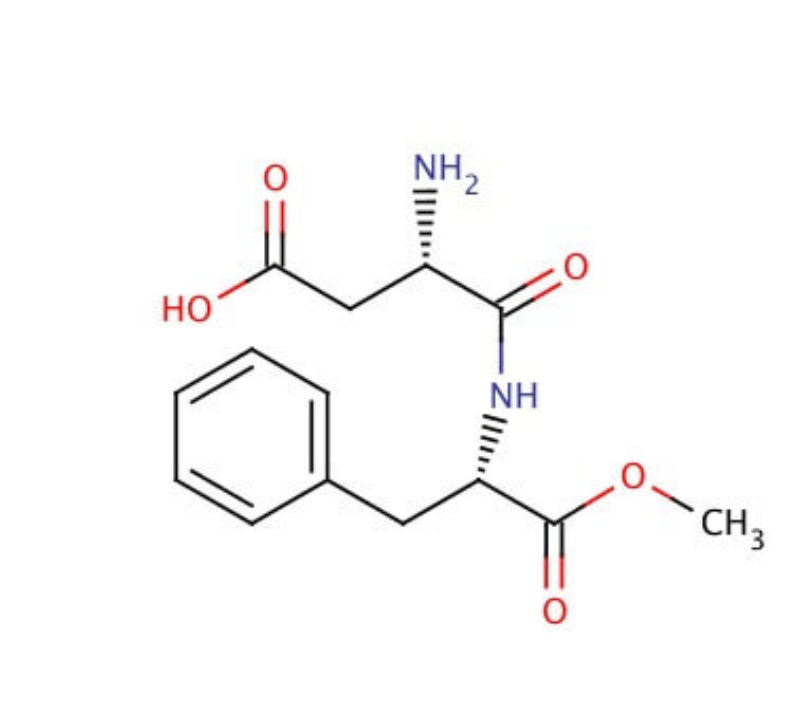
Aspartame Cas number:22839-47-0 Molecular Formula: C14H18N2O5
Aspartam
Aspartame
Asp-Phe Methyl Ester
Equal
H-Asp-Phe-Ome
L-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine Methyl Ester
L-Asp-Phe Methyl Ester
N-L-Alpha-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine 1-Methyl Ester
N-L-Alpha-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine Methyl Ester
Nutrasweet
(S)-3-Amino-N-((S)-1-Methoxycarbonyl-2-Phenyl-Ethyl)-Succinamic Acid
1-Methyln-L-Alpha-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine
3-Amino-N-(Alpha-Carboxyphenethyl)Succinamicacidn-Methylester
3-Amino-N-(Alpha-Carboxyphenethyl)Succinamicacidn-Methylester,Stereoisome
3-Amino-N-(Alpha-Methoxycarbonylphenethyl)Succinamicacid
Aspartylphenylalaninemethylester
Canderel
Dipeptidesweetener
L-Phenylalanine,N-L-.Alpha.-Aspartyl-,1-Methylester
| Melting Point | 242-248 °C |
| Density | 1.2051(rough estimate) |
| storage temp | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature 2-8°C |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble or slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in hexane and in methylene chloride. |
| optical activity | N/A |
| Appearance | White Powder |
| Purity | ≥98% |
Aspartame is the most popular artificial sweetener in the United States. It is sold as sweeteners such as NutraSweet and Equal, but it is also incorporated into thousands of food products.
Aspartame is a high-intensity sweetener that is a dipeptide, provid- ing 4 cal/g. it is synthesized by combining the methyl ester of phenylalanine with aspartic acid, forming the compound n-l-alpha- aspartyl-l-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester. it is approximately 200 times as sweet as sucrose and tastes similar to sugar. it is compara- tively sweeter at low usage levels and at room temperature. its mini- mum solubility is at ph 5.2, its isoelectric point. its maximum solubility is at ph 2.2. it has a solubility of 1% in water at 25°c. the solubility increases with temperature. aspartame has a certain insta- bility in liquid systems which results in a decrease in sweetness. it decomposes to aspartylphenylalanine or to diketropiperazine (dkp) and neither of these forms is sweet. the stability of aspartame is a function of time, temperature, ph, and water activity. maximum stability is at approximately ph 4.3. it is not usually used in baked goods because it breaks down at the high baking temperatures. it contains phenylalanine, which restricts its use for those afflicted with phenylketonuria, the inability to metabolize phenylalanine. uses include cold breakfast cereals, desserts, topping mixes, chew- ing gum, beverages, and frozen desserts. the usage level ranges from 0.01 to 0.02%.